Introduction: The Foundation of Well-Being
Think of your body as a finely tuned orchestra, and your hormones are the conductors. These chemical messengers travel throughout your bloodstream, coordinating everything from your mood and metabolism to your sleep and stress response.
When this intricate system is in sync, you experience a state of vibrant health and well-being. However, even a subtle disruption can throw everything off key. This is the essence of hormonal balance—a state where your body’s messengers are working in harmony, ensuring every system functions as it should.
Achieving optimal hormonal balance is not about a quick fix; it’s a holistic approach that builds the foundation for long-term health. In this guide, we’ll explore the key pillars—diet, lifestyle, and self-awareness—that can help you take control and restore this crucial balance.
Recognizing the Signs of Hormonal Imbalance
It’s easy to overlook subtle symptoms, but your body often sends clear signals when something is off. A hormonal imbalance can manifest in a variety of ways, some of which may seem unrelated at first. For women, common indicators often involve the menstrual cycle. This can include irregular periods, unexpected spotting, or even a complete absence of menstruation.
Beyond the cycle, you might notice unexplained weight gain, especially around the midsection, despite no significant changes to your diet or exercise routine. Acne that appears on the chin, jawline, or back is another classic sign, as are mood swings, persistent fatigue, and trouble sleeping.
Paying close attention to these symptoms is the first step toward understanding your body’s needs and taking action to restore your hormonal balance.
Diet as a Cornerstone for Hormonal Balance
What you eat is one of the most powerful tools you have to influence your body’s chemistry. The right nutrients provide the raw materials for hormone production, while a poor diet can trigger inflammation and stress, throwing off your hormonal balance. Focus on incorporating healthy, whole foods into your daily routine.
Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil, are essential building blocks for hormones. Lean protein from sources like fish, chicken, and legumes helps stabilize blood sugar and reduces the hunger hormone, ghrelin. And don’t forget fiber! It’s crucial for gut health, which in turn plays a significant role in hormone regulation.
Conversely, minimizing processed foods, refined sugars, and excessive caffeine can prevent the insulin spikes and cortisol surges that disrupt the delicate dance of your hormones.
Lifestyle Factors for Sustaining Hormonal Balance
Beyond what you eat, your daily habits have a profound impact on your body’s delicate chemical network. Stress management is paramount. When you’re stressed, your body produces cortisol, the “fight-or-flight” hormone.
While useful in short bursts, chronically high cortisol levels can disrupt your entire endocrine system, affecting everything from your thyroid function to your reproductive hormones. Incorporating practices like mindfulness, deep breathing, or yoga can help keep cortisol in check.
The power of sleep cannot be overstated. Your body uses the time you’re asleep to repair, detoxify, and regulate hormone production. Lack of quality sleep can lead to insulin resistance and elevated cortisol, directly compromising your hormonal balance. Aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted rest to give your body the time it needs to reset.
Finally, regular exercise is a vital tool for supporting a healthy metabolism and promoting hormonal balance. Physical activity helps your cells become more sensitive to insulin, which is key to managing blood sugar.
It also reduces stress hormones and boosts endorphins, contributing to a sense of well-being. The key is consistency and finding a form of movement you enjoy, whether it’s a brisk walk or a high-intensity workout.
A Closer Look at Hormonal Balance for Fertility
For many, the topic of hormonal balance becomes a primary focus when trying to conceive. Your body’s ability to reproduce is a complex, hormone-driven process that depends on synchronized communication between your brain and your ovaries.
Key players in this process include follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which prompts the ovaries to prepare an egg, and luteinizing hormone (LH), which triggers ovulation. Estrogen is responsible for building the uterine lining, while progesterone prepares the body for a potential pregnancy.
When this communication is disrupted, fertility can be impacted. Conditions like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) are a prime example. PCOS is characterized by a significant hormonal imbalance that can lead to irregular or absent ovulation, affecting the ability to get pregnant. Other conditions, like thyroid disorders, can also throw off the delicate balance needed for conception.
Fortunately, supporting your hormonal balance can be a proactive step in your fertility journey. This includes many of the same principles already discussed, such as a nutrient-dense diet and stress reduction.
Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight and understanding your cycle through methods like basal body temperature tracking can offer valuable insights into your body’s rhythms and help you take control of your reproductive health.
The Gut-Hormone Connection
The gut microbiome is a complex ecosystem of bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms. A healthy gut is crucial for overall health, and its connection to hormonal balance is a growing area of research. This relationship is so significant that the gut is sometimes called the “second brain.”
The gut plays a key role in regulating hormones in several ways. For instance, the estrobolome, a collection of gut bacteria, helps metabolize and manage the circulation of estrogen. An unhealthy gut can lead to an overproduction or under-elimination of estrogen, contributing to conditions like estrogen dominance.
The gut’s health is also directly linked to insulin sensitivity. An imbalance in gut bacteria, known as dysbiosis, can lead to chronic inflammation and compromise the integrity of the gut lining. This can contribute to insulin resistance, a condition where your body’s cells don’t respond effectively to insulin, which can throw off your blood sugar and other hormones.
To support a healthy gut for improved hormonal balance, consider these dietary strategies:
- Probiotic-rich foods: Fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi introduce beneficial bacteria to your gut.
- Prebiotic fibers: Found in foods like garlic, onions, asparagus, and bananas, prebiotics feed the good bacteria already in your gut.
- Whole foods: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides a wide variety of fibers that support a diverse and healthy microbiome.
- Avoid inflammatory foods: Limiting refined sugars, processed oils, and artificial sweeteners can help reduce inflammation and maintain gut integrity.
Section 6: The Interplay of Hormones and Mental Health
The connection between your hormones and your mental state is far more intricate than many people realize. Hormones don’t just regulate physical functions; they are chemical messengers that directly influence your mood, emotions, and cognitive function. This is a two-way street: a hormonal imbalance can cause or worsen mental health issues, and chronic mental stress can, in turn, disrupt your hormone levels.
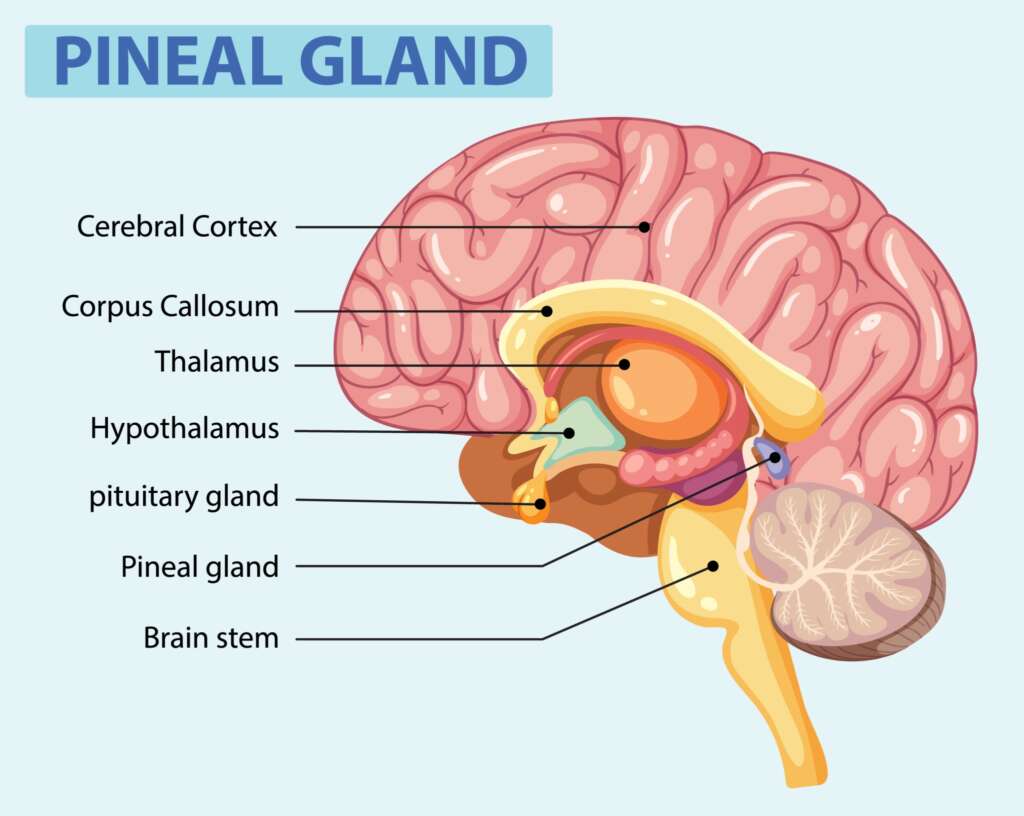
For example, when you’re under chronic stress, your adrenal glands continuously pump out cortisol. While short bursts of cortisol are healthy for a “fight or flight” response, prolonged high levels can wreak havoc.
Over time, high cortisol can deplete your serotonin and dopamine levels—the neurotransmitters responsible for feelings of happiness and pleasure. This can contribute to feelings of anxiety, fatigue, and depression. It can also impair your memory and concentration, leading to that common “brain fog” feeling.
The female reproductive cycle is another prime example of this interplay. The monthly fluctuations of estrogen and progesterone can significantly impact mood.
For some women, this can lead to premenstrual syndrome (PMS) or, in more severe cases, premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD), which is characterized by debilitating mood swings, irritability, and depression. A sudden drop in these hormones after childbirth can also contribute to postpartum depression, highlighting their profound impact on emotional well-being.
Your thyroid hormones are also major players. An underactive thyroid, or hypothyroidism, is a common condition where the thyroid gland doesn’t produce enough hormones.
This can lead to symptoms that mirror depression, such as persistent fatigue, lack of motivation, and a general feeling of sadness. These symptoms are often misdiagnosed as purely psychological when in reality, they are a direct consequence of a hormonal imbalance.
Understanding this connection is crucial for holistic wellness. By addressing the underlying hormonal balance through diet, sleep, and stress management, you can create a more stable environment for your mental health.
This is why lifestyle changes can be so effective in managing anxiety, depression, and mood swings—they are powerful tools for restoring equilibrium from the inside out.
Navigating Hormonal Changes Through Life Stages
Your hormonal balance is not a static state; it is a dynamic system that shifts and adapts throughout your life. Understanding these natural transitions can empower you to proactively support your health and well-being.
The Early Years and Reproductive Prime: The hormonal rollercoaster begins with puberty, as the body ramps up production of sex hormones like estrogen and testosterone. The menstrual cycle itself is a finely tuned dance of hormones.
When ovulation occurs, a spike in estrogen can boost energy and mood, while the subsequent rise in progesterone can have a calming effect. Conversely, a drop in these hormones before menstruation can lead to irritability and other common PMS symptoms. Being aware of this monthly rhythm can help you anticipate and manage these mood shifts.
Pregnancy and Postpartum: Pregnancy is arguably the most dramatic hormonal shift in a woman’s life. Hormones soar to incredible levels to support the growing fetus, which can lead to everything from morning sickness to mood swings.
After birth, these hormones plummet just as suddenly, which can be a key factor in the development of postpartum depression. Supporting the body with nutrient-dense foods and adequate rest during this time is critical.
The Mid-Life Transition: Perimenopause and Menopause: For women, the years leading up to menopause are a period of significant hormonal change. Perimenopause is marked by fluctuating hormone levels as the ovaries gradually wind down their function. This can result in unpredictable periods, night sweats, hot flashes, sleep disturbances, and mood swings.
Once a woman has gone 12 consecutive months without a period, she is officially in menopause. While these changes are natural, they can be challenging. A balanced diet, consistent exercise, and stress-reduction techniques can help mitigate many of these symptoms.
Andropause (Male Hormonal Changes): Men also experience a gradual decline in hormone production, primarily testosterone, a process sometimes referred to as andropause. This decline is more subtle than menopause but can lead to a decrease in muscle mass, lower energy levels, and changes in mood. Maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular strength training can help support healthy testosterone levels.
Understanding these life-stage-specific hormonal balances allows you to approach your health journey with knowledge and intention. It emphasizes that while some shifts are inevitable, you have the power to influence how your body responds and adapts.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Hormonal Balance
Achieving and maintaining hormonal balance is a dynamic process, not a destination. It’s a journey of listening to your body, understanding its signals, and providing it with the support it needs. As we’ve explored, the foundation for this balance lies in three key pillars: a nutrient-rich diet, mindful lifestyle choices, and a deeper understanding of your body’s internal systems, particularly the gut.
By prioritizing healthy fats, managing stress, getting enough sleep, and moving your body regularly, you aren’t just treating symptoms; you’re addressing the root causes of imbalance. This holistic perspective is the key to unlocking true well-being.
While these strategies are powerful, remember they are complements to, not replacements for, professional medical advice. If you suspect a serious imbalance, a doctor can provide the guidance and testing you need. Ultimately, taking control of your hormonal balance is about empowering yourself to live a healthier, more vibrant life.
What is a hormonal imbalance?
A hormonal imbalance occurs when there is too much or too little of a specific hormone in your bloodstream. Since hormones act as messengers regulating nearly every bodily function, even a slight imbalance can cause widespread symptoms.
When should I see a doctor about my hormones?
You should consider consulting a healthcare provider if you experience persistent symptoms of a hormonal imbalance, such as irregular periods, unexplained weight changes, significant mood swings, or if you have been trying to conceive without success for an extended period. A doctor can perform tests to diagnose the issue and recommend a personalized treatment plan.
What foods should I avoid to maintain hormonal balance?
To maintain a healthy hormonal balance, it’s generally recommended to limit or avoid highly processed foods, sugary drinks, and refined carbohydrates, as these can trigger inflammation and insulin spikes. Excessive caffeine and alcohol consumption can also negatively impact your hormone levels.
What are some natural ways to treat a hormonal imbalance?
Many lifestyle changes can help restore hormonal balance. These include a diet rich in whole foods and healthy fats, getting 7-9 hours of quality sleep, engaging in regular exercise, and practicing stress management techniques like meditation or yoga.
Can a hormonal imbalance affect my fertility?
Yes, a hormonal imbalance is one of the most common causes of female and male infertility. In women, it can disrupt the menstrual cycle and ovulation, and in men, it can affect sperm production and quality. Conditions like PCOS, thyroid disorders, and hyperprolactinemia are all linked to hormonal imbalances that impact fertility.